草食性昆虫によって食い物にされるトウモロコシの鉄獲得戦略
草食性昆虫によって食い物にされる植物の鉄獲得戦略
要旨
草食性昆虫は宿主から多量元素や微量元素を得ている。そこで我々はトウモロコシに特化した害虫であるwestern corn rootworm(トウモロコシ根食いセンチュウ?)が、どのようにして植物由来の微量元素を見つけてそれに近づくのかを調べた。この根を食する小動物はトウモロコシを宿主として認識するためにトウモロコシの2次代謝産物類である「鉄・benzoxazinoid」を利用し、根の中に侵入して生長するという戦略をとっていることを見出した。トウモロコシは同様のBenzoxazinoid類を普通の根圏寄生動物からの防御に使っていると同時に、本論文で示すように自分自身の鉄吸収のために使っている。corn rootwormが持つ「鉄・benzoxazinoid」を吸収するトランスポーターも同定した。したがって植物由来の「微量元素・二次代謝産物」をあさることはトウモロコシとそれに特化した植食者の間の適応的な相互作用であるといえる。
Plant iron acquisition strategy exploited by an insect herbivore
L. Hu1, P. Mateo1,2, M. Ye1, X. Zhang1, J. D. Berset1, V. Handrick3*, D. Radisch3,
V. Grabe3, T. G. Köllner3, J. Gershenzon3, C. A. M. Robert1†, M. Erb1†
Hu et al., Science 361, 694–697 (2018) 17 August 2018
Insect herbivores depend on their host plants to acquire macro- and micronutrients. Here we asked how a specialist herbivore and damaging maize pest, the western corn rootworm, finds and accesses plant-derived micronutrients. We show that the root-feeding larvae use complexes between iron and benzoxazinoid secondary metabolites to identify maize as a host, to forage within the maize root system, and to increase their growth. Maize plants use these same benzoxazinoids for protection against generalist herbivores and, as shown here, for iron uptake. We identify an iron transporter that allows the corn rootworm to benefit from complexes between iron and benzoxazinoids. Thus, foraging for an essential plant-derived complex between a micronutrient and a secondary metabolite shapes the interaction between maize and a specialist herbivore.
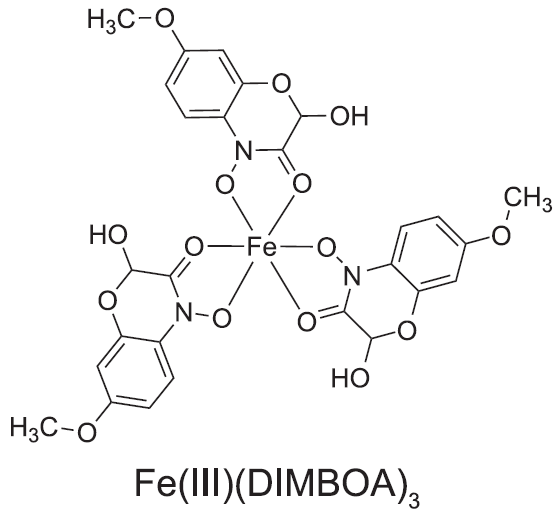
トウモロコシ根が鉄欠乏で分泌する化合物とその3価鉄キレート化の状態